Most mobile carriers transmit SMS as unencrypted data across their networks and store messages in plain-text format. Despite this, many of us still use SMS to receive One-Time Passwords (OTPs) for our most sensitive accounts–from banking to social media and more. That’s because nothing beats SMS in terms of convenience, and many services mandate it as the only option for identity verification.
Because SMS messages travel in plain text, anyone who intercepts them can read them instantly, leaving us vulnerable to a range of threats:
- SS7 or Signaling Attacks: Attackers can exploit flaws in global roaming protocols to trick the system into rerouting your SMS directly to them.
- Rogue Base Stations: Stingrays or IMSI catchers impersonating legitimate towers can trick your phone into connecting to them. Once connected, they can “see” your SMS traffic as it passes through.
- Compromised Infrastructure: Even legitimate, certified telecom base stations can be compromised. In 2025, Korean authorities disclosed a nearly “undetectable” compromise of femtocells (mini-base stations) that allowed hackers to intercept SMS and hijack financial accounts.
- Malicious Apps: If a malicious app gains SMS permissions, it can read your messages directly from your device, where they are stored without protection.
At Cape, we’ve always believed that security and convenience shouldn’t be mutually exclusive.
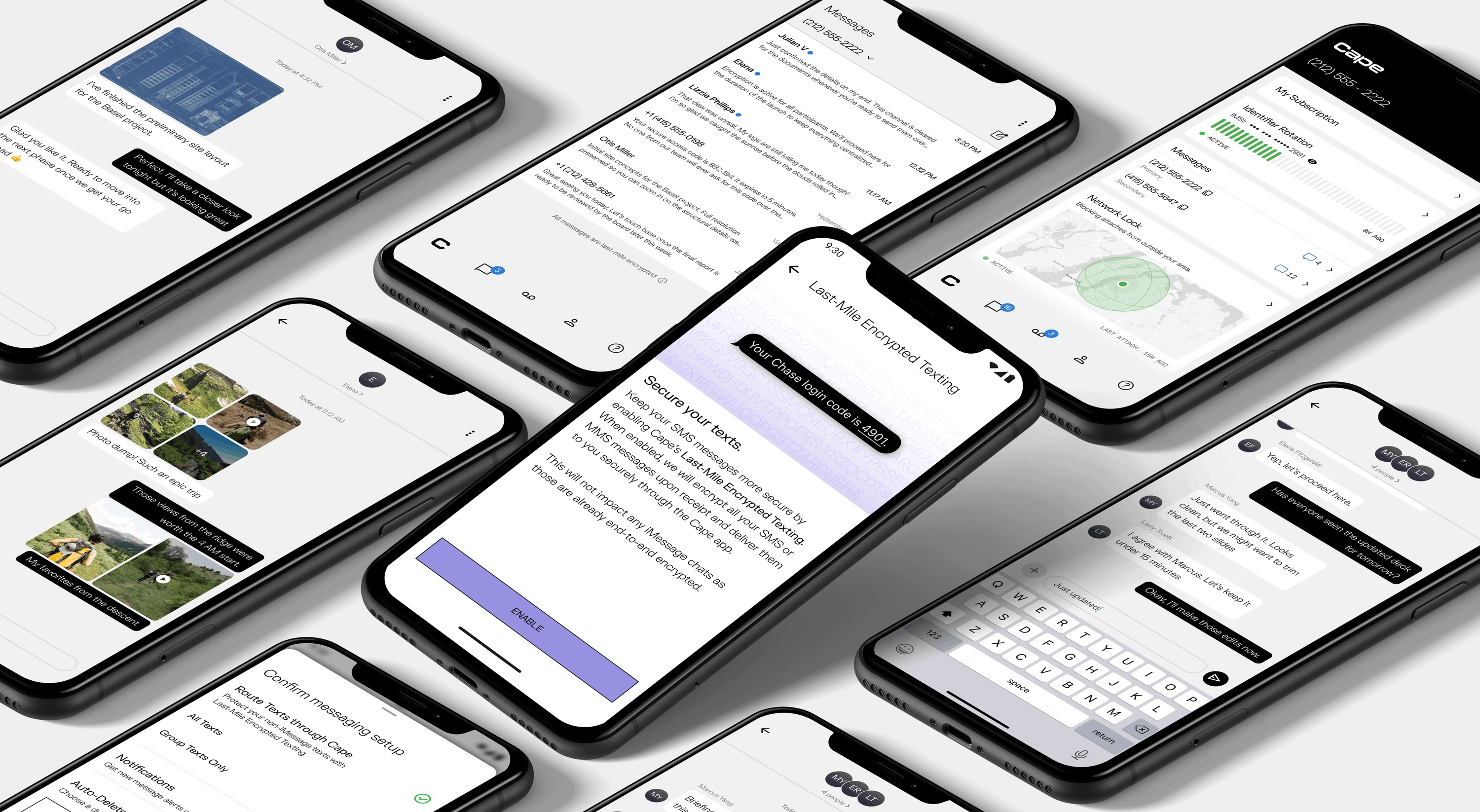
We’re excited to introduce Last-Mile Encrypted Texting. While true end-to-end encryption isn’t possible for SMS (as the protocol required decryption for carrier interoperability), we’ve engineered a middle-to-end encryption layer for greater defense-in-depth.
When Last-Mile Encrypted Texting is enabled:
- Cape encrypts your SMS and MMS messages the moment we receive them, and delivers them securely through the Cape app. Even if your SMS were intercepted somewhere between Cape and your phone, it’s unreadable without the private key stored on your device.
- Our physical infrastructure partners cannot see or log your SMS/MMS messages.
- You can optionally set your messages to auto-delete after 1, 7, or 30 days.
Important Notes
- Last-Mile Encrypted Texting is available on iPhone only. We are working on enabling it for other devices soon.
- Last-Mile Encrypted Texting only applies to SMS/MMS messages. iMessage will continue to route to your native iMessage app, as they are already end-to-end encrypted.
- Last-Mile Encrypted Texting will prevent group chats in your iPhone’s Messages app that include Android members from becoming de-threaded (when messages are sent or received individually, instead of as part of the group thread.) We are working towards a longer-term solution for group chat de-threading for iPhone users, but for now, Last-Mile Encrypted Texting will ensure your group chats work as expected.
- We are actively working to bring RCS (Rich Communication Services) to Cape. While RCS 3.0 is beginning to introduce end-to-end encryption between iPhone and Android, this standard is currently limited by carrier adoption and OS-level rollouts. Most importantly, most service providers still send highly sensitive data, like bank OTPs, via legacy SMS, which RCS does not yet cover. We plan to roll out full RCS support later this year as mobile operating systems and carriers expand their compatibility.
How to get started
On January 27th, 2026, Cape exited our beta and launched several new features, including Secondary Numbers, Secure Global Roaming, and Identifier Rotation (for iPhone & Pixel). For our other new features, you can find access instructions here.